How to Cure Parkinson’s Disease
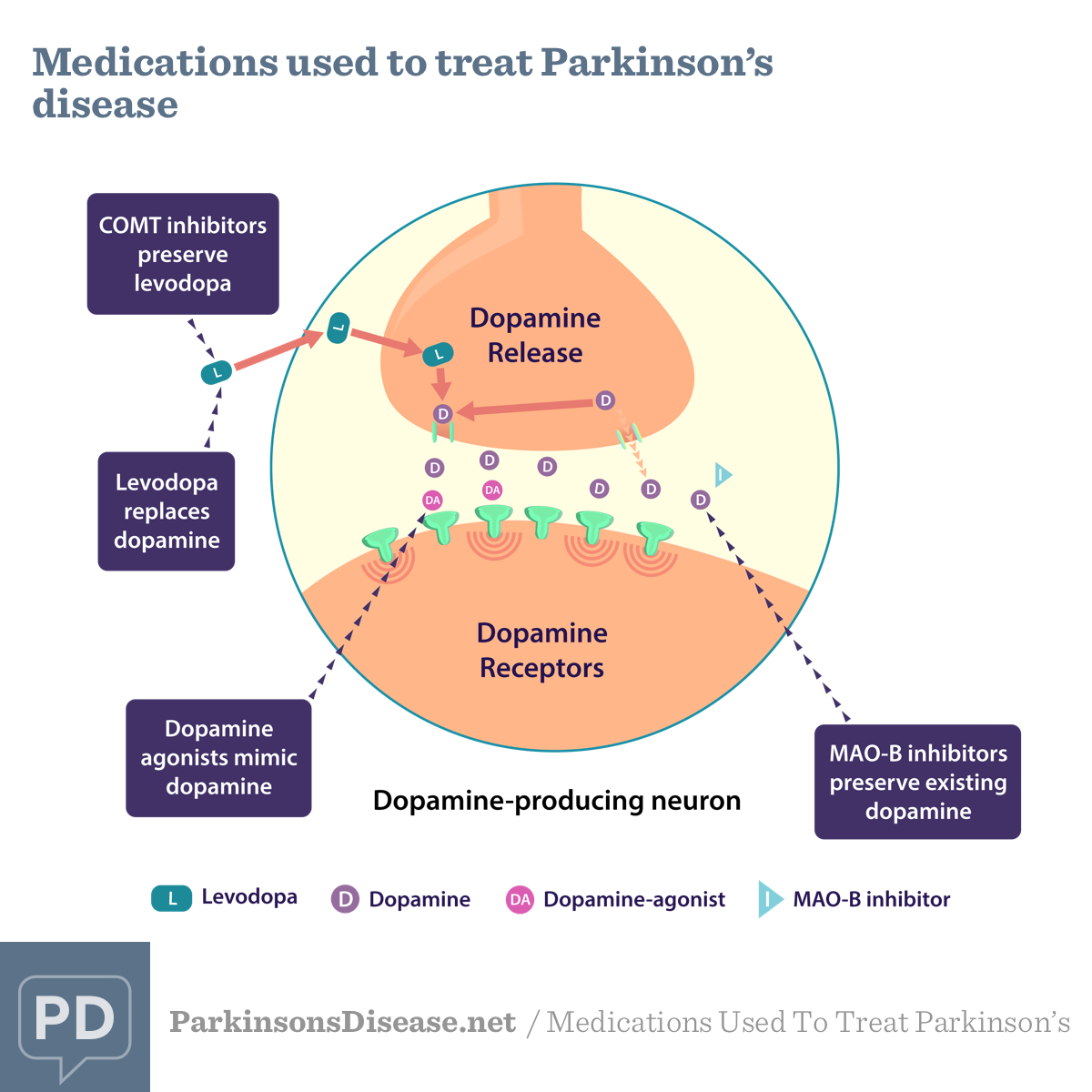
The first step in curing Parkinson's disease is understanding the symptoms and knowing what you should do to manage the symptoms. The most common treatments involve medications that block the breakdown of dopamine, or increase the production of dopamine. Other treatment options involve surgery. As early as the 1940s, doctors attempted to correct the disorder by surgically removing portions of the brain, including the cerebral cortex. Newer procedures target the basal ganglia and deliver dopamine-producing enzyme directly to the gene that controls movement.
The next step in treating Parkinson's disease is preventing symptoms and managing the condition. Although medications are the most common treatment option, they may no longer work well in some patients. Some medications help patients with symptoms during the "on" period, while other drugs cause side effects and may not provide relief. In rare cases, medication may not work as intended. In these cases, medication changes may be necessary. In more severe cases, patients may need to undergo surgical procedures to cure the disease.
Medications can also help manage the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. The most common medications are based on the effects of dopamine on the central nervous system, which allows the brain to communicate with the rest of the body. However, some patients find the medications ineffective. During an "on" period, the medication reduces the symptoms; however, it doesn't reduce symptoms during an "off" period. If the medications are no longer working, surgery might be the only option.
Medications are the most common treatment option for patients with Parkinson's disease. These drugs work by stimulating the substantia nigra cells to produce more dopamine and inhibiting the production of acetylcholine. These drugs work by restoring the balance between two chemicals in the brain. For each patient, an individual treatment plan is drawn up with the attending physician, since the side effects of different drugs vary. If symptoms persist, medication may need to be changed. In more severe cases, the disease may require surgery.
Medications are the most effective treatment option for most patients with Parkinson's disease. The drugs work by stimulating the substantia nigra cells to produce more dopamine and inhibiting the production of acetylcholine. These medications are effective, but some patients experience a "off" period where the medications do not improve symptoms. As with any medication, the best treatment plan depends on your specific health condition.
Drugs are not a cure for Parkinson's disease. They can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. For some patients, medications may not be effective. But others still require surgery. The goal of a successful operation is to eliminate the symptoms of the disease as much as possible. But medication can help. Fortunately, most people with Parkinson's disease are treated with various types of medications. While there is no single cure for Parkinson's disease, medications can improve a patient's quality of life.
Medicines for Parkinson's disease are the most effective treatments for the disease. Depending on the severity of your symptoms, medications can help you maintain a good quality of life. Medications can reduce the stiffness and tremors experienced by patients. Although there is no cure for the disease, these medicines can control the symptoms. If you are intolerant to medications, you can also opt for surgical procedures to relieve the illness.
In addition to medication, doctors may recommend physical therapy and occupational therapy. Occupational therapy can help you learn to speak and hear again, and speech therapy can improve your balance. Some patients with Parkinson's disease may also need surgery. But if medications are not effective, it is better to choose other treatment options. The author's website Buu Lam has several other treatments that can help you live a normal life.
Drug treatment of Parkinson's disease is the most common treatment. Medications may be effective for a while, but they can also become ineffective over time. Also, medications may not work properly, reducing symptoms during "on" periods but not during "off" periods. As a result, patients will have to change their medications. If these methods are ineffective, surgery may be required. If medications are not enough to treat symptoms, they will need to undergo deep brain surgery.
Leave a Reply