Chikungunya Causes Joint Pain
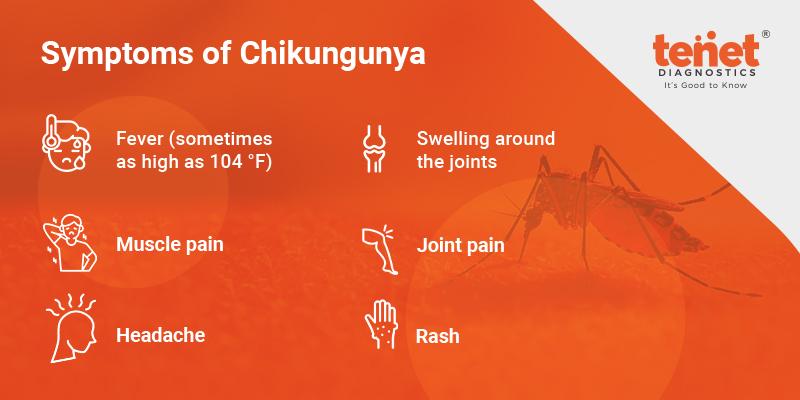
While the chikungunya virus rarely causes a life-threatening infection, it can have unpleasant effects, including severe joint pain. While the fever usually goes away within a week, the aches and pains from the disease can last for months, even years. A recent study found that 20 percent of people with the virus suffer from repeated joint pains after a year. If you experience such long-term joint aches and pains, physiotherapy can help you recover.
The name chikungunya derives from a Makonde root verb, kungunyala, which means to bend up or get contorted. Robinson glossed the word, which translates as "that which bends up." Subsequent authors assumed that the word was derived from Swahili, the language of the region. Despite the similarities between the two diseases, they have very different symptoms.
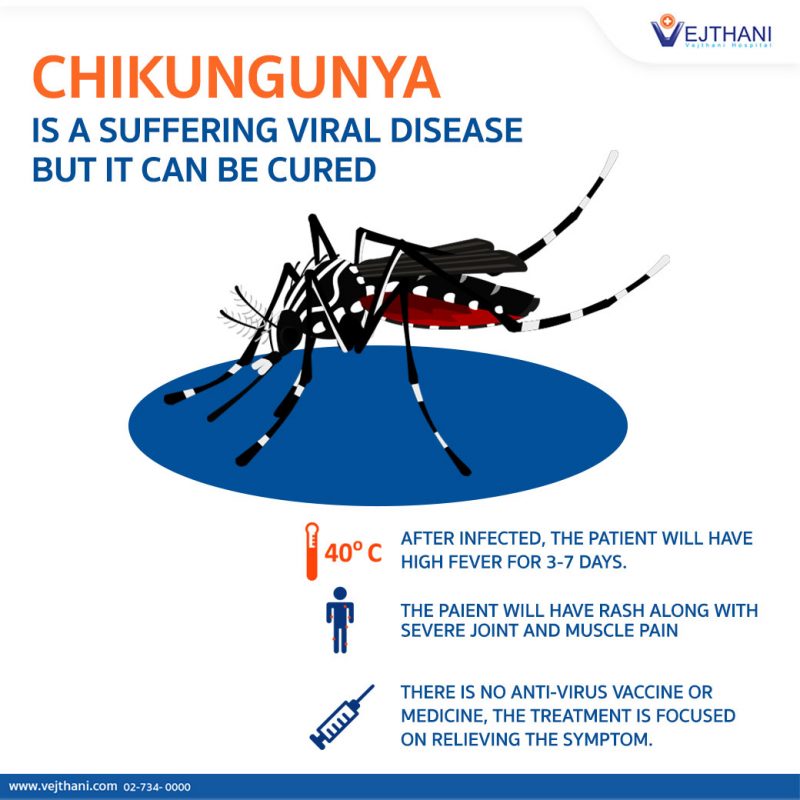
The first recorded cases of the disease occurred in Tanzania in 1952. The virus belongs to the family of viruses called alphaviru s. The name chikungunya comes from the Kimakonde language and means "to become contorted." Sufferers of the disease are typically stooped and may experience severe joint pain and fever. The virus is found in more than 60 countries, including the United States, Canada, Mexico, and Australia.
The Chikungunya virus is spread through a mosquito bite. While it is not contagious, it can be transmitted to humans through the contact of infected blood. There is no vaccine against the chikungunya virus, and it is not recommended that you contact a mosquito if you are infected with it. And if you’ve ever been bitten by a mosquito, you know what it feels like.
The disease is caused by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which can be found in many parts of the world. The infection is characterized by sudden, intense joint pain and fever, which can last for a few days or even weeks. Infected individuals may experience severe muscle aches and joint swelling, but they don’t require medication. Most patients recover on their own, and there is no need for hospitalization.
The virus is a single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus that has been circulating around the world for several centuries. The virus is a member of the Alphavirus family and belongs to the Semliki Forest Virus serogroup, which also includes Ross River virus, Mayaro virus, and O’nyong-nyong virus. While the symptoms of chikungunya can vary from person to person, the disease is common throughout the world.
Children and adolescents are more susceptible to the disease than adults, but there is no cure for the disease. Most people will experience joint pain and fever and should seek medical attention as soon as possible. The disease can also be misdiagnosed as rheumatoid arthritis, but symptoms are often mild. Once an infection is diagnosed, patients may experience fever, joint pain, or conjunctivitis.
In addition to being bitten by mosquitoes, people with chikungunya should avoid being bitten by mosquitoes for the first week after contracting the disease. This is because the virus can circulate in a person’s blood for up to a week after exposure. It can also spread to other people. The virus can be transmitted through the air, so it’s important to stay away from infected areas.
The virus can also cause ocular, neurological, or gastrointestinal complications. It can be fatal for older patients, but most people make a full recovery on their own. However, joint pain can last for months. Chikungunya symptoms include joint pain and fever. These symptoms often go undiagnosed and are misdiagnosed due to other mosquito-borne diseases. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Although this disease is not life-threatening, it can cause severe joint pain. The symptoms are similar to dengue fever and the Zika virus, so they can be hard to tell apart. Those who live in mosquito-infested areas are at risk of developing the disease. It is best to seek medical attention immediately after contracting the virus to avoid any complications. If you become infected, you must consult a doctor for treatment and visit the site cth.co.th
for more information about therapy.
Symptoms of the disease usually appear three to seven days after a mosquito bite. Some people may experience joint pain, joint swelling, or muscle pain. Other symptoms may be more severe and may last for months or years. The virus is contagious and cannot be prevented, but it can be treated with conventional medicines. Because there is no vaccine for chikungunya, treatment depends on antibodies to the virus.
Leave a Reply